SEO: How Reputation Has Become an Important Ranking Factor
The guidelines of Google Quality Rating seem to be increasingly relevant after the latest updates and if you want to be top in search engines you can no longer ignore the reputation acquired and that you will succeed in acquiring online.
Chris Smith, president of Argent Media, had predicted everything you will read in this article back in 2007 when he said that Google could use the quality scoring for organic rankings, proposing a whole series of changes to be made to the websites, mainly focused on quality factor.
According to Google, over the years Google would have applied a Quality Score, identifying factors such as a page “about us” that is precise and detailed, a contact page that introduces trust, good usability and user experience, clear use of copyright and a good spelling and grammar, just some of the fundamental factors that we then saw to have been the path taken by Google for the evolution of the algorithm.
The most recent edition of Google’s “Quality Evaluators Guideline”, also called “Quality Rating Guideline” (“QRG”) is almost a script of its previous recommendations regarding quality factors.
Google’s “Quality Rating Guidelines” are increasingly relevant after the latest updates
Discordant voices also from official Google sources seem to bounce on the importance or not of the reputation, going from the same Danny Sullivan who confirmed that the evaluations of the human evaluators are not used in the automatic learning of the algorithms, while Marie Haynes explained how it considers that the elements mentioned in the guidelines for quality assessment may be factors that influence the ranking, such as a company’s BBB ranking and the reputation of the authors.
At the same time, Googlers have increasingly advised webmasters to “focus only on quality”, and even recommend webmasters to read QRGs to offer the best possible content, just as Sullivan himself did when he officially commented on the updates of the basic algorithm of last October.
But then how does Google determine the quality in an algorithmic way starting from the concepts of competence, authority, reliability, and reputation that seem very subjective?
The Google algorithms have to translate these concepts into measurable criteria that can be measured and compared between sites/pages competing.
Chris Smith believes that some of Google’s previous algorithmic developments probably point towards this process, interpreting a certain degree of disconnection between what people asked and how the various Googlers responded and how people themselves interpreted these answers.
If Google instructs its human raters to evaluate the EAT (Expertise, Authority, and Trust) of a site but does not incorporate the resulting evaluations, what is the algorithm that uses the algorithm?
Simply stating that the algorithm uses a collection of things like a BBB assessment, user reviews or link trust analysis, even if that answer seems too limited. Also, to say that Google provides a quality assessment based solely on link trust analysis and query analysis seems too limited.
That’s why by deduction we could say that Google is obviously taking into account some factors that go beyond a more advanced analysis of links/queries, even if this still remains a fundamental part of the mix.
The website quality patent from Google
One of the many Google patents we talked about months ago is based on machine learning. Noted by Bill Slawski it is the ” Website Quality Signal Generation “. In synopsis, it said how human beings could be used to assess the quality of websites, and therefore the analysis algorithm could associate those evaluations with website signals, probably automatically identifying the relationships between quantified signals and values of human evaluation, generating models with characteristic signals. These signal patterns could then be used to compare signals with other websites not evaluated to apply quality scores to them.
The wording is rather fascinating: “Raters connect to the Internet websites and rate of quality of the websites. The raters can submit quality ratings to server analysis through the rating input device. The quality analysis server receives website quality ratings the website quality ratings are associated with a uniform resource locator and other website signals corresponding to the rated website. The quality analysis server identifies relationships between website quality ratings and website signals and creates a model representing relationships, as described below.
As you will have noticed some of the same things mentioned above are mentioned in the QRG. But this is not the reason why the patent is so convincing, but because it provides a very logical framework in which to develop methods to evaluate the quality of websites and web pages, and to generate a Quality Score that can be used in the determinations of ranking. The methods in question indicate that relatively small sets of test pages could be used to create models that could work well on all other similar or similar pages.
Imagine that you have identified a type of page for which you want to create a quality score, such as an informative article on a health topic. Google could take the signals we mentioned earlier including the amount of content, page layout, number of ads and ad placement on the page, site reviews, reviews and links to content created on other sites, the links off the page (perhaps indicating the identity of the content creator and / or citing reference information sources), site and page links (PageRank), clickthrough rates the page from its first keyword searches, the correspondence of the title visible at the top of the page with the content of the page and the title of the research fragment and the meta description as well as the factors that indicate that the site is up-and-up.
By testing numbers of similar page types, Google may have developed a model of combining quality signals and developed a score value associated with it.
In essence, when a page of an article on a health topic has a certain range of criteria such as PageRank, plus a certain layout of the content, plus a certain PageRank, plus CTR, more user reviews, plus lots of other factors then Google could apply the calculated Quality Score on the page without any human being reviewing it manually.
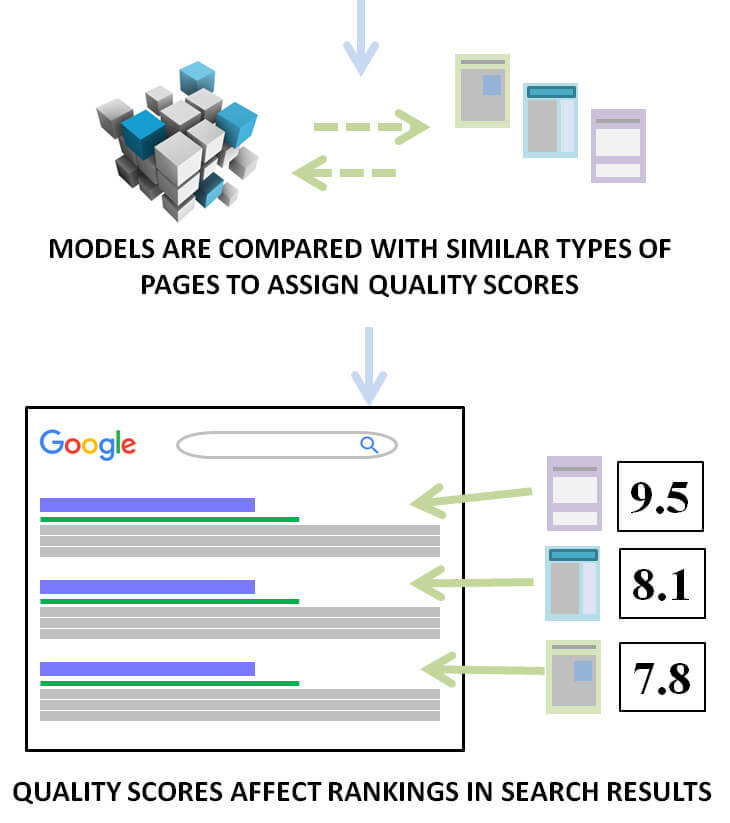
Interpreting the diagram published above with a broader interpretation, we could hypothesize that thanks to automatic learning the system could identify more complex relationships (like assigning a certain quality score if the PageRank is N to NN, CTR is X to XX, coupled with a specific type of page layout) and not, for example, saying that an article on a health topic evaluated with a certain level of quality assessment should have a minimum PageRank of X, a minimum number of links, etc. .
In fact, it is the same patent that describes this possibility, right when he says that “in some implementations, the model can be derived from the web site signals and from the web site quality assessment using a submachine learning that implements a support vector regression “.
In essence, this produces an automatic learning classifier. The model can, therefore, be used to identify all the pages of a common class, calculate a quality score and then apply the same or similar evaluation to other pages of the same class and/or category.
Many other SEO analysts have long been saying that Google is incorporating machine learning into content rankings (see Eric Enge and Mark Traphagan), and not just in interpreting the queries that Google has publicly revealed.
This really explains some of the inconsistencies we have seen in Google’s search results for months. The neural networks seem to produce very holistic scores, so aim for any signal or even a handful of signals that most influence the outcome in a given case would probably not really possible.
The various possible signals that probably incorporate the Quality Score also have a certain complexity
- PageRank – and/or some evolved signal that can also involve the quality/trust of links;
- User Reviews Sentiment – Google’s QRG suggests that there would be a certain threshold of reviews, so if a business/website had relatively few total reviews, they could most likely be rated as unrepresentative. So, if Google is incorporating reputation, how else could they adjust the ranking if they don’t do some kind of sentiment analysis? Of all the rather nebulous quality assessments, the feeling is relatively simple to analyze and use.
- Mention Sentiment – Do people mention a product in social media and e-mail? The “buzz” of social media is a measure of popularity and even feeling can be a measure of quality.
- Click-Through-Rate (CTR) – (and relative bounce rate) there was a lot of debate about this potential factor over time, but like the Quality Score itself, if used by the Quality Score of the ads, why not also for organic rankings?
- On the other hand, if it is only a part of a website’s Quality Score, then CTR is not a direct ranking factor and this could explain the discrepancies in the search results.
- Percentage of Ad Placements – How much of the total space on the page consists of ads? Google may have calculated a minimum / maximum threshold. Also, how many ads are on a page and how much do they split the main content of the page? Are there gaps or overlaps that cannot be closed? Do the ads follow while scrolling the page?
- Missing sites Identification information- Sites should ideally have “About” and “Contact Us” pages. About the sections, they should explain who the company is and, even better, list the most important staff members along with the photos. The “contacts” page should ideally have as much contact information as possible, including addresses, phone numbers, and contact submission forms. It probably helps if the staff pages are linked to employee social media and LinkedIn profiles and vice versa. There is nothing worse than visiting a site and not being able to see who’s behind it!
- Critical E-Commerce and Financial Site Factor- The HTTPS protocol is a fact – but it is also true that Google goes beyond the simple checking-off if you have HTTPS but since not all configurations and encryption are the same as E-Commerce and financial information sites must also have clear Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy and customer service contact information. In addition, they must include the Help sections and the Goods Return Policies. Even if Google does not use the trust badge as a quality factor, it is still important to have it to reassure consumers online and can increase sales by increasing trust.
- Site speed – this is almost taken for granted, but it has always been a factor in the PPC Quality Score, and it is still a type of quality measurement in organic research.
How the PageRank Score calculation method could be used
Another interesting aspect of how the Quality Score could work is that the Quality Score of a page could also incorporate the Quality Score of the other pages that link to it or to its domain.
The Quality Score could partly be calculated by iterating over the entire graph of the link a number of times in the calculation of the scores, using a method similar to the original algorithm of PageRank. This would produce a more weighted scale of the Quality Score values, helping to ensure that the highest quality content is truly at the top, completely burying the lowest quality content to the point where research is virtually never encountered in typical interactions of research.
Comments on some sites affected by Medic Update
Barry Schwartz published a handful of sites affected by the Medic Update, and observing them it was noted that most of the above criteria were missing as the potential quality factors and that the QRG specifically mentions:
- com – He had no page. Infinite scroll. The “Contact Us” page was on a different domain. A reputation of article writers not necessarily experts in medical subjects. Very large ads and lateral grotesque and distracting badges.
- org – Redirect, cartoon images on the staff page, no text, no phone/address. The contact form appears only after a human click of validation.
- com – Customer service contact telephone number that is difficult to locate and that can be connected to a subdomain.
- com – Information on the page redirects to the homepage! No phone/address /personal address. There was also a strange graphics code of the logo.
Mixed messages with respect to ranking signals
Some of the potential signals we have mentioned have been quite controversial but they could rightly explain why there is a major divergence on what some SEO professionals believe are classification factors and what the Googlers argue.
Chris Smith also believes that the Googlers sometimes played a semantic game. The presence of one or more controversial factors (CTR, sentiment analysis, etc.) is not direct ranking factors because these factors may or may not turn into a complex assessment that results in a Quality Score. And he continues his thoughts by saying that, for example, “if my conjectures on the Quality Score are close to how it works, then two different pages on the same topic could be very similar and both have a high CTR, but the Quality Score of one or two could be significantly higher due to a combination of other factors. In other cases, still, a higher CTR could move a page upwards to be classified at a higher quality level “.
A model of a good quality page sounds like a ” search recipe “, as Danny Sullivan himself defined it. There are therefore different combinations and weightings of the factors used to determine the quality scores of the different types of pages.
And that’s why, taking up the holistic concept mentioned in the article, Chris Smith defines Quality Score as a gesture. This is why Googlers have recommended unclear changes for sites affected by the latest updates, such as “working to improve overall quality” and “focusing on making the best possible content”. Apart from technical SEO problems, it is rarely possible to change one or two things throughout the site to improve low-quality scores. As Glenn Gabe observed on the sites affected by these changes, “site owners should not look for a single smoking gun, as there is almost never one.”
How to improve the quality score of your site
How can knowing that Quality Score is a complex Gestalt can help improve the ranking?
The good news is that most of the SEO guidelines are still very current. A good SEO approach must always reside in the technical SEO construction, keeping error pages and pages without content to a minimum. Eliminate pages of thin and superfluous content. Avoid prohibited link building practices.
SEO itself is a holistic practice, and as such it constantly needs to be done all the things that are appropriate and reasonably feasible to optimize any website. That’s why it’s important to use great online SEO tools for your website optimization.
Certainly, all the elements that reassure consumers are of vital importance: information on the pages, on the contact pages, on the pages of the Privacy Policy and on the Terms and Conditions, contact options of the customer service, as well as, if necessary, updating the contents.
Nothing should be left to chance, displaying the site as if you were a user, trying to completely satisfy the needs of real users, responding to negative reviews and trying to get online reviews from satisfied users/customers.
Finally, it is necessary to practice proactive reputation management working to positively involve the community, both online and offline, in a coherent way over time. Engage with social media and develop your presence through these channels. Provide free good advice as online experts to build your reputation. Become a member of professional groups in your sector and community groups. Respond in a professional way and don’t fall into online provocations.
So here we are at the end, remembering that all these practices will generate the signals for a good quality score over time and the benefits will soon arrive.
Author Bio
Wanda Mooree run’s professional SEO authority services firm in Texas. Also spends a lot of his free time educating the minds of thousands of young Texas SEO and top agencies. She is a featured author at various authoritative blogs in the health and fitness industry and currently associated as a blogger with Justseotech.com





























